Computational Geomechanics
The contributions in this area include the computational mechanics and geomechanics (non-linear finite elements), coupled analysis (flow in deformable media), nonlinear constitutive theories for geomaterials along with hydraulic fracturing, propagation of cracks in medium, geotechnical earthquake engineering and Soil-Structure interactions heterogeneous media. The research projects that have been done in this area consist of studying the behavior of an integral abutment bridge and a rockfill dam using numerical modeling. The former project is financially founded by Louisiana Department of Transportation and Development for the investigation on the substructure of the Caminada Bay Bridge in Louisiana, USA. The former project includes studying the performance of a Taleghan dam in Iran. The financial support of this project is provided by the Ministry of Energy of Iran.
1. Integral Abutment Bridge for Louisiana’s Soft and Stiff Soils: Caminada Bay Bridge
A 3D finite element (FE) model is developed to study the behavior of different parts of the Integral Bridge Abutment under different types of loads and temperature changes. The FE model includes the study of (1) piles, embankment/backfill, abutment, and deck (2) behavior of the backfill material and surrounding soil under the cyclic abutment displacement; (3) pile and soil interaction; (4) abutment wall and soil interaction; (5) slab and soil interaction (may not be applicable); (6) settlement of soil and its effect on the slab design, and (7) effect of temperature and longitudinal movement.
Numerical simulation is performed using ABAQUS/Standard software which provides extensive tools for 3D modeling, powerful constitutive models for soil, and is capable of modeling the interaction of two different media.
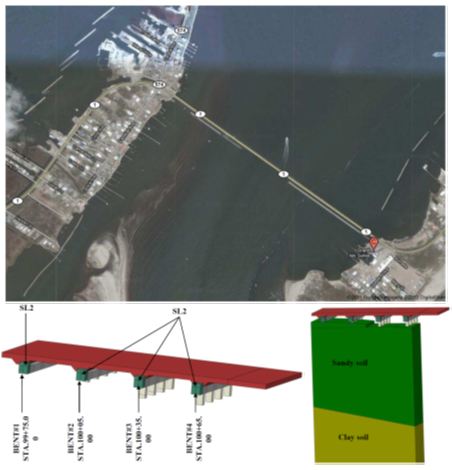
Approaching slab (super structure) is considered a continuous part which is rigidly connected to the bents. Based on the experimental results of bore holes, the modeled soil is divided to two parts. The upperpart of the soil which mainly consists of sand is considered as granular soil and the lower part is considered as fine grain material which is mostly composed of clay.
2. Investigating the effect of the first impounding on the behavior of the Taleghan dam
The objective of this research is to study the behavior of a case study rock-fill dam with a clay core using Finite element method using more complicated material modeling. The 2D and 3D Finite Element Analyses are performed to investigate the behavior of Taleghan Dam during construction and first impounding using ABAQUS software. The mathematical framework adopted in the analysis is based on a formulation that couples the equations of flow of pore water and deformation for a porous media. Finally the results of the analyses and comparison with measured data are presented.
Special attention is paid to the two most important phenomena which might happened during the first impounding of the rockfill dams: The collapse of upstream shell and hydraulic fracturing of the clay core.
The collapse settlement of the upstream rock fill shell is modeled in the analyses of the first impounding. Furthermore, the occurrence of the hydraulic fracturing in the clay core is investigated using a proposed tensile criterion. With considering the tensile criterion and shear plastic strain zone, the more trusted safety factor against hydraulic fracturing in the clay core of the studied dam is obtained. Finally, the results of the analyses compared with the measured data in the dam.